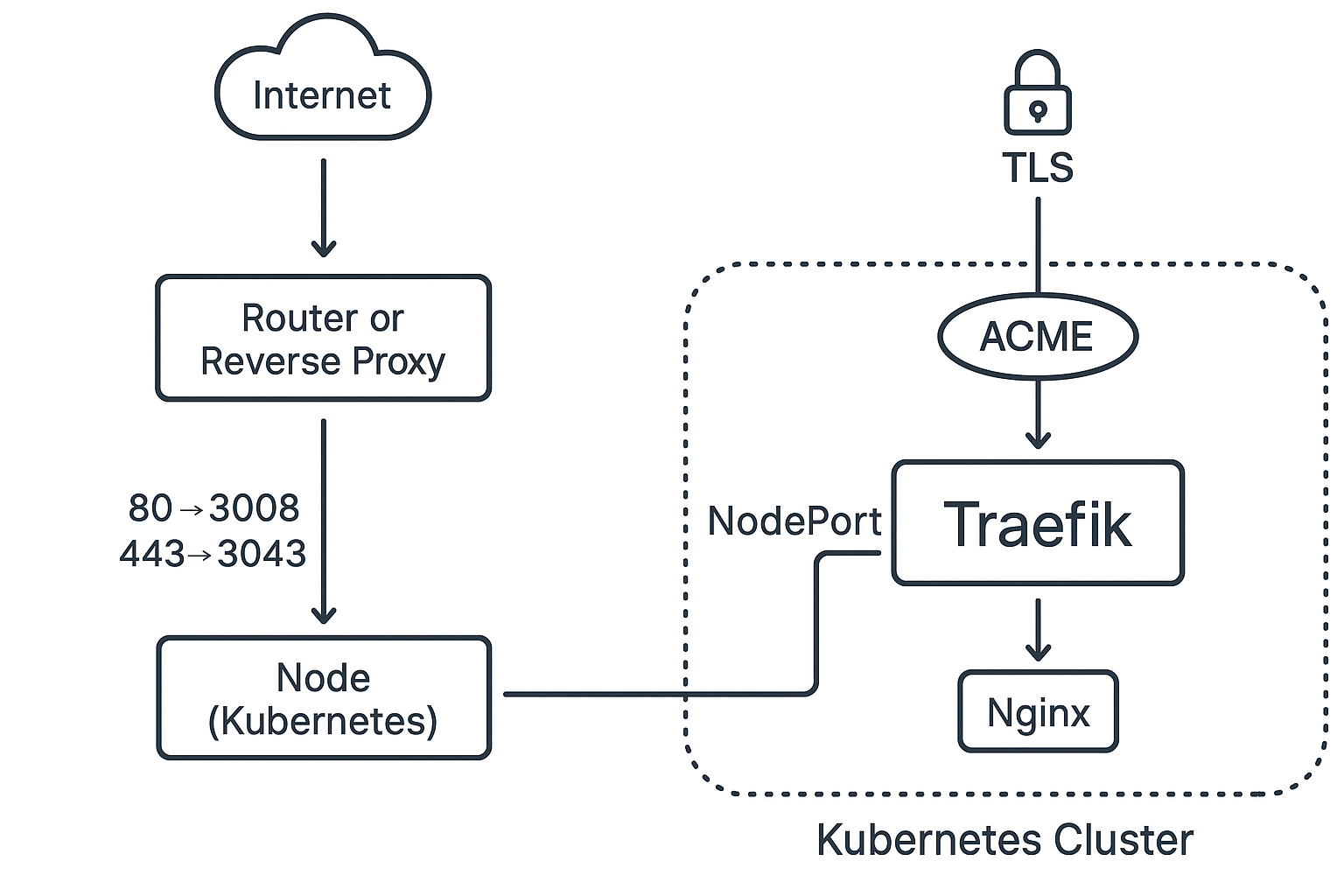
Self Hosted K8s Networking
To expose Traefik on one IP using NodePort and route external traffic through it, follow this step-by-step setup. This is ideal when you don’t have a cloud provider or want to control traffic using your own router, Nginx reverse proxy, or something like Cloudflare Tunnel.
✅ Step-by-Step: Expose Traefik via NodePort and Use One External IP
1. Deploy Traefik via Helm with NodePort
If you’re using Helm (recommended):
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts
helm repo update
Install Traefik with NodePort enabled:
helm install traefik traefik/traefik \
--namespace kube-system --create-namespace \
--set service.type=NodePort \
--set service.ports.web.nodePort=30080 \
--set service.ports.websecure.nodePort=30443
This will:
- Deploy Traefik in
kube-systemnamespace. -
Expose:
- HTTP on port
30080 - HTTPS on port
30443
- HTTP on port
2. Get Node IP (External or Internal)
You need the IP of one of your Kubernetes nodes (ideally the one with internet access):
kubectl get nodes -o wide
Pick the EXTERNAL-IP (or INTERNAL-IP if behind NAT/router).
3. Set DNS or External Proxy to Point to That Node
Now route all traffic to that IP:
Option A: From Your Router (Port Forwarding)
- Forward port
80→NODE_IP:30080 - Forward port
443→NODE_IP:30443
Option B: With NGINX (if installed on a VM or external host)
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://NODE_IP:30080;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name your-domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_pass https://NODE_IP:30443;
}
}
Option C: Cloudflare Tunnel (Optional)
If you want to expose Traefik securely without public IP, you can use a Cloudflare Tunnel:
cloudflared tunnel create traefik
cloudflared tunnel route dns traefik your-domain.com
# In config.yml
tunnel: traefik
credentials-file: /etc/cloudflared/traefik.json
ingress:
- hostname: your-domain.com
service: http://NODE_IP:30080
- service: http_status:404
4. Deploy Ingress or IngressRoute
Here’s a basic Ingress example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: whoami
namespace: default
annotations:
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.entrypoints: web
spec:
rules:
- host: whoami.your-domain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: whoami
port:
number: 80
You can also use IngressRoute if you’re using CRDs.
🔁 Summary
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| NodePort | Exposes Traefik inside the cluster |
| Node External IP | Used by clients to access services |
| Reverse Proxy / Router | Forwards 80/443 to 30080/30443 |
| Ingress Rules | Tell Traefik how to route traffic |
Here’s a complete example of how to deploy NGINX inside your Kubernetes cluster, expose it using a ClusterIP Service, and then configure Traefik to forward traffic to it using an Ingress.
✅ Step 1: NGINX Deployment + Service (ClusterIP)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:stable
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
✅ Step 2: Traefik Ingress to Forward to NGINX
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
namespace: default
annotations:
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.entrypoints: web
spec:
rules:
- host: nginx.localhost
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
💡 Note: Replace
nginx.localhostwith your real domain name. You can test it locally with/etc/hostslike:127.0.0.1 nginx.localhost
✅ Step 3: Access NGINX via Traefik
- If you’re using NodePort, Traefik is listening on
http://<NodeIP>:30080. - If using LoadBalancer, Traefik is on a public IP.
-
Then:
- Visit
http://nginx.localhost(with DNS or/etc/hostspointing to the Node IP) - Traefik will route it to the internal NGINX service.
- Visit
To configure Traefik with ACME (Let’s Encrypt) for automatic TLS certificate generation, follow these steps. This setup enables Traefik to request and renew certificates automatically.
🛠️ 1. Traefik Deployment with ACME Enabled
✅ Helm (Recommended)
If you’re using Helm to deploy Traefik, add the following to your values.yaml:
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
websecure:
address: ":443"
certificatesResolvers:
letsencrypt:
acme:
email: [email protected]
storage: /data/acme.json
httpChallenge:
entryPoint: web
volumes:
- name: acme-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: traefik-acme-pvc
volumeMounts:
- name: acme-storage
mountPath: /data
Or directly with Helm CLI:
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm install traefik traefik/traefik \
--namespace traefik --create-namespace \
--set ports.websecure.exposed=true \
--set ports.web.exposed=true \
--set certificatesResolvers.letsencrypt.acme.email=[email protected] \
--set certificatesResolvers.letsencrypt.acme.storage=/data/acme.json \
--set certificatesResolvers.letsencrypt.acme.httpChallenge.entryPoint=web \
--set persistence.enabled=true \
--set persistence.name=acme-storage \
--set persistence.accessMode=ReadWriteOnce \
--set persistence.size=1Gi
This creates a persistent volume to store
acme.jsonso certs are retained across pod restarts.
🧾 2. IngressRoute with Let’s Encrypt TLS
Here’s how you define an IngressRoute that uses the ACME resolver (letsencrypt):
apiVersion: traefik.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
entryPoints:
- websecure
routes:
- match: Host(`nginx.example.com`)
kind: Rule
services:
- name: nginx
port: 80
tls:
certResolver: letsencrypt
📁 3. Required Permissions
Make sure the directory where acme.json is stored is writable by the Traefik pod. If using a PVC, you’re good. If mounting manually:
touch acme.json
chmod 600 acme.json
Mount it as a volume:
volumeMounts:
- name: acme
mountPath: /data
volumes:
- name: acme
hostPath:
path: /etc/traefik/acme
✅ 4. DNS and Port Forwarding
- Ensure your domain (e.g.,
nginx.example.com) points to your Traefik LoadBalancer IP. - Port 80 must be accessible to solve the ACME HTTP-01 challenge.
🧪 5. Verify
Check the logs:
kubectl logs -n traefik deploy/traefik
You should see logs showing certificate acquisition like:
... obtained certificate for domain nginx.example.com